Are you looking to strengthen your core and improve your posture? The Roman chair might be the perfect tool for you.
But what muscles does a Roman chair target exactly? Understanding which muscles get worked can help you make the most of your workouts and avoid injury. Keep reading to discover how this simple piece of equipment can transform your fitness routine and help you build a stronger, more balanced body.

Roman Chair Basics
The Roman chair is a simple piece of equipment. It helps strengthen your lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. This exercise tool also targets your core muscles. Using it correctly can improve your posture and reduce back pain.
Understanding how to set up and use the Roman chair is key. Proper form keeps you safe and makes the exercise effective. Let’s explore the basics.
Equipment Setup
Place the Roman chair on a flat, stable surface. Adjust the foot pads so your ankles fit snugly. Your thighs should rest comfortably on the upper pads. Make sure the equipment does not wobble before starting.
Proper Form
Keep your back straight and core tight. Bend at the hips, not the waist. Lower your upper body slowly until you feel a stretch. Raise your body back up with control. Avoid jerky movements to protect your spine.
Primary Muscles Worked
The Roman chair is a simple tool that targets key muscles in your lower body and back. It helps build strength and stability. Knowing the primary muscles worked can improve your workout focus. These muscles work together to support your posture and movement.
Erector Spinae
The erector spinae muscles run along your spine. They help you stand tall and keep your back straight. Using the Roman chair strengthens these muscles. This support reduces the risk of back pain. Strong erector spinae muscles improve balance and posture.
Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in your buttocks. It controls hip movement and helps you stand up from sitting. The Roman chair activates this muscle during back extensions. Strengthening the gluteus maximus improves power and stability. It also helps in activities like running and climbing.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings are a group of muscles at the back of your thighs. They bend your knees and extend your hips. The Roman chair engages these muscles as you lift your upper body. Strong hamstrings support knee health and boost leg strength. They also help prevent injuries during exercise.
Secondary Muscles Engaged
The Roman chair mainly works the lower back and glutes. Yet, it also activates other muscles. These secondary muscles help keep the body steady and support movement. They improve balance and control during the exercise.
Core Stabilizers
The core stabilizers include muscles around the stomach and lower back. They keep your body steady while you bend and lift. These muscles stop you from wobbling or falling. Strong core stabilizers improve posture and reduce injury risk.
Hip Flexors
Hip flexors help lift your legs and bend your hips. They assist during the Roman chair movement by controlling your lower body. Engaging these muscles improves hip strength and flexibility. This support helps you perform the exercise smoothly and safely.
Exercise Variations
The Roman chair offers several exercise variations to target different muscle groups. Each variation focuses on specific muscles, helping improve strength and stability. These exercises work the lower back, glutes, and core. Trying different moves keeps workouts fresh and effective.
Back Extension
The back extension is the most common Roman chair exercise. It mainly targets the lower back muscles, called the erector spinae. This move strengthens the spine and improves posture. Keep your body straight and lift your upper body slowly. Avoid bending your neck to reduce strain.
Side Bends
Side bends focus on the oblique muscles along your waist. These muscles help with twisting and bending movements. To do side bends, position yourself sideways on the Roman chair. Slowly lower your upper body to one side, then lift it back up. This exercise improves core strength and balance.
Reverse Hyperextensions
Reverse hyperextensions target the glutes and hamstrings. Lie face down on the Roman chair with your hips at the edge. Lift your legs behind you while keeping them straight. This movement builds hip strength and supports lower back health. Perform slow, controlled lifts for best results.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Using the Roman chair correctly helps build strong muscles safely. Many people make simple errors that reduce the exercise’s benefits. Avoiding these mistakes keeps your lower back safe and improves your workout results. Focus on proper form to target the right muscles effectively.
Overextending The Back
Overextending the back puts too much strain on your spine. This mistake can cause pain or injury. Stop when your body is in a straight line. Do not bend too far backward. Controlled movements engage muscles better and protect your back.
Incorrect Foot Placement
Placing your feet incorrectly reduces stability and power. Your feet should be firmly locked in the foot pads. Too high or too low foot placement changes how muscles work. Correct foot position helps maintain balance and focus on target muscles.
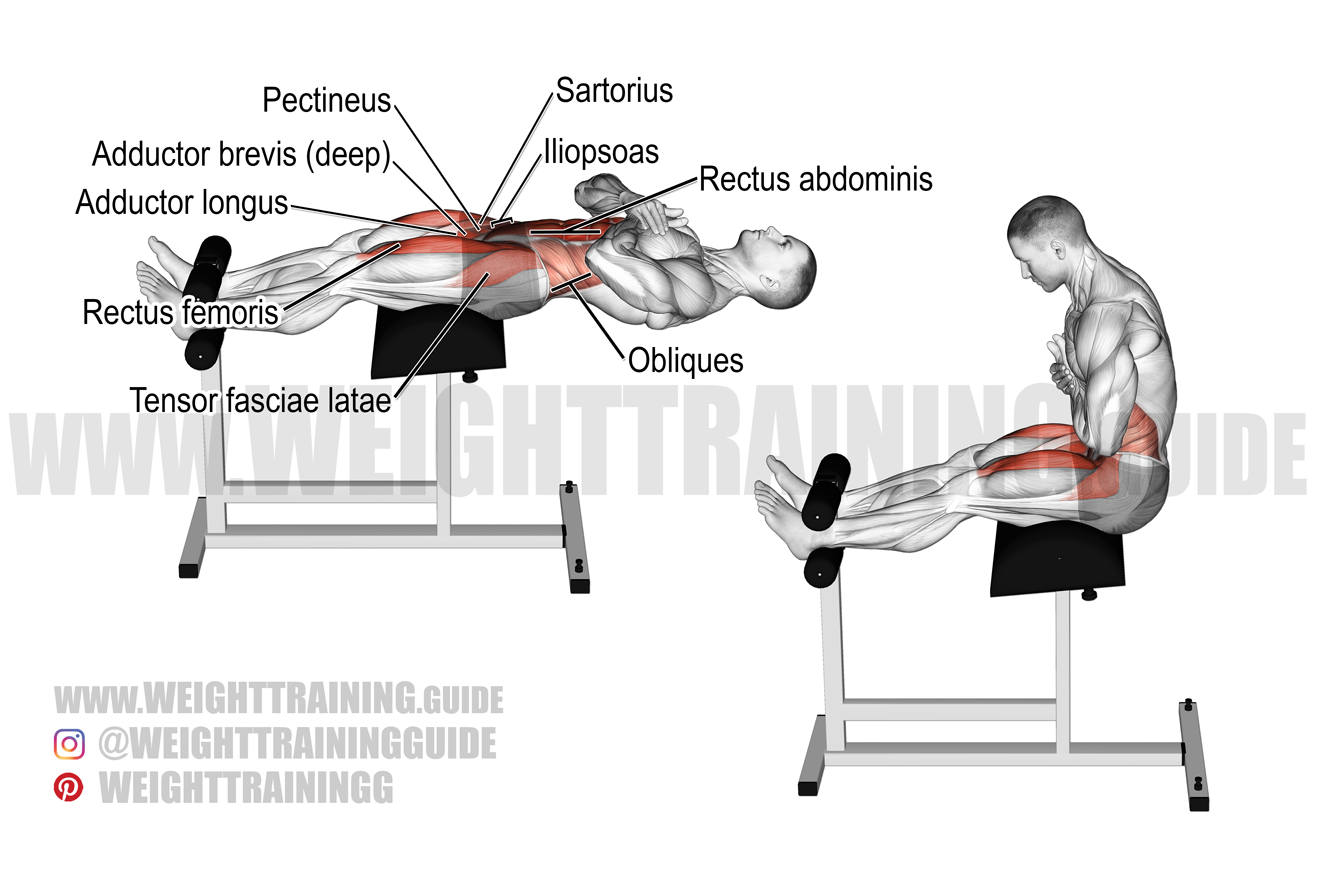
Benefits For Strength And Stability
The Roman chair exercise builds strength and stability in key muscle groups. It targets muscles in the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. Strengthening these areas helps support daily movements and reduces injury risk. Stability improves balance and control in many physical activities.
Regular use of the Roman chair improves core strength. A strong core supports the spine and enhances overall body control. This leads to better performance in both exercise and everyday tasks.
Improved Posture
The Roman chair helps correct poor posture by strengthening the back muscles. Stronger muscles hold the spine in a healthy position. This reduces slouching and back pain. Good posture also boosts confidence and appearance. Sitting and standing become easier with a strong back.
Enhanced Athletic Performance
A strong lower back and core improve athletic skills. They provide power for running, jumping, and lifting. Stability from these muscles helps prevent falls and injuries. Athletes gain better control and endurance. The Roman chair supports training for many sports.
Injury Prevention Tips
Using a Roman chair can strengthen your back and core muscles well. But exercising without care may cause injuries. Following injury prevention tips keeps your workout safe and effective. Focus on proper preparation and gradual progress.
Warm-up Routines
Start each session with a warm-up. This prepares your muscles and joints. Do light cardio for 5 to 10 minutes. Try walking or gentle cycling. Follow with dynamic stretches like leg swings and arm circles. Warm muscles reduce the risk of strains. Warming up also improves your exercise performance.
Progressive Overload
Increase exercise difficulty slowly over time. Begin with easier Roman chair moves. Add more reps or hold positions longer. Raise the challenge step by step. Avoid sudden jumps in intensity or volume. Progressive overload helps muscles adapt safely. This method lowers the chance of injury and boosts strength.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Primary Muscles Does A Roman Chair Work?
The Roman chair mainly targets the lower back muscles, specifically the erector spinae. It also engages the glutes and hamstrings, helping strengthen these areas for better posture and core stability.
How Does The Roman Chair Benefit Core Strength?
Using the Roman chair improves core strength by activating the lower back and abdominal muscles. It enhances spinal support, reduces injury risk, and promotes overall core endurance and balance.
Can A Roman Chair Improve Posture?
Yes, the Roman chair strengthens the muscles that support proper posture. It builds the lower back and glute muscles, which helps maintain spinal alignment and reduces slouching.
Are Roman Chair Exercises Good For Hamstrings?
Roman chair exercises effectively engage and strengthen the hamstrings. This improves leg stability, flexibility, and overall lower body strength, benefiting athletic performance and injury prevention.
Conclusion
The Roman chair works many muscles in your back and core. It strengthens the lower back, glutes, and hamstrings. This exercise helps improve posture and balance. Using the Roman chair regularly builds muscle and prevents injuries. It suits beginners and experienced exercisers alike.
Try adding it to your workout for better strength. Keep your movements slow and controlled for best results. The Roman chair targets key muscles for a strong, stable body. Simple but effective.

